
PPT Vedic Literature PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5538364
Veda, (Sanskrit: "Knowledge") a collection of poems or hymns composed in archaic Sanskrit by Indo-European-speaking peoples who lived in northwest India during the 2nd millennium bce.No definite date can be ascribed to the composition of the Vedas, but the period of about 1500-1200 bce is acceptable to most scholars. The hymns formed a liturgical body that in part grew up around the soma.

Vedic literature Atharva Veda Mind map
Vedic Sanskrit corpus The term "Vedic texts" is used in two distinct meanings: Texts composed in Vedic Sanskrit during the Vedic period ( Iron Age India) Any text considered as "connected to the Vedas" or a "corollary of the Vedas" [33] The corpus of Vedic Sanskrit texts includes:

Forty Aspects of Veda And Vedic Literature Vol. 1 & 2 Maharishi Vedic Pandits Amazon.in Music}
The details of the Total Knowledge charts allows one to focus on the pure knowledge and be centered on 'A' and not get lost in the relative aspects.. the togetherness of Silence and Dynamism. The Vedic literature is what is humming in my own transcendental consciousness. The sounds express sequentially. Each of the 40 areas of the Veda.

Later Vedic Period Timeline, Map and Religion
asura Dyaus Vedic religion, the religion of the ancient Indo-European-speaking peoples who entered India about 1500 bce from the region of present-day Iran. It takes its name from the collections of sacred texts known as the Vedas. Vedism is the oldest stratum of religious activity in India for which there exist written materials.

Vedic chart or Vedic Scriptures chart Suppliments, Vedas, Bhagavad Gita, Flow Chart, Sutra
The Vedas are one of the oldest Hindu scriptures and contain a collection of hymns, liturgical formulas, and prayers. In Vedic literature UPSC notes, we will discuss what Shruti and Smriti Vedic Literature is, the key differences between early Vedic literature and later Vedic literature, along with different types of Vedic literature.
1.3 The Role of Scriptures
The Vedic literature constitutes the fulcrum of Sanskrit literature and is repositories of some fundamental concepts of human rights. This manuscript endeavors to decode the tenets of human rights concealed in the Vedic texts.

The People Living of Early Vedic (Rigvedaic Age) and Later Vedic HubPages
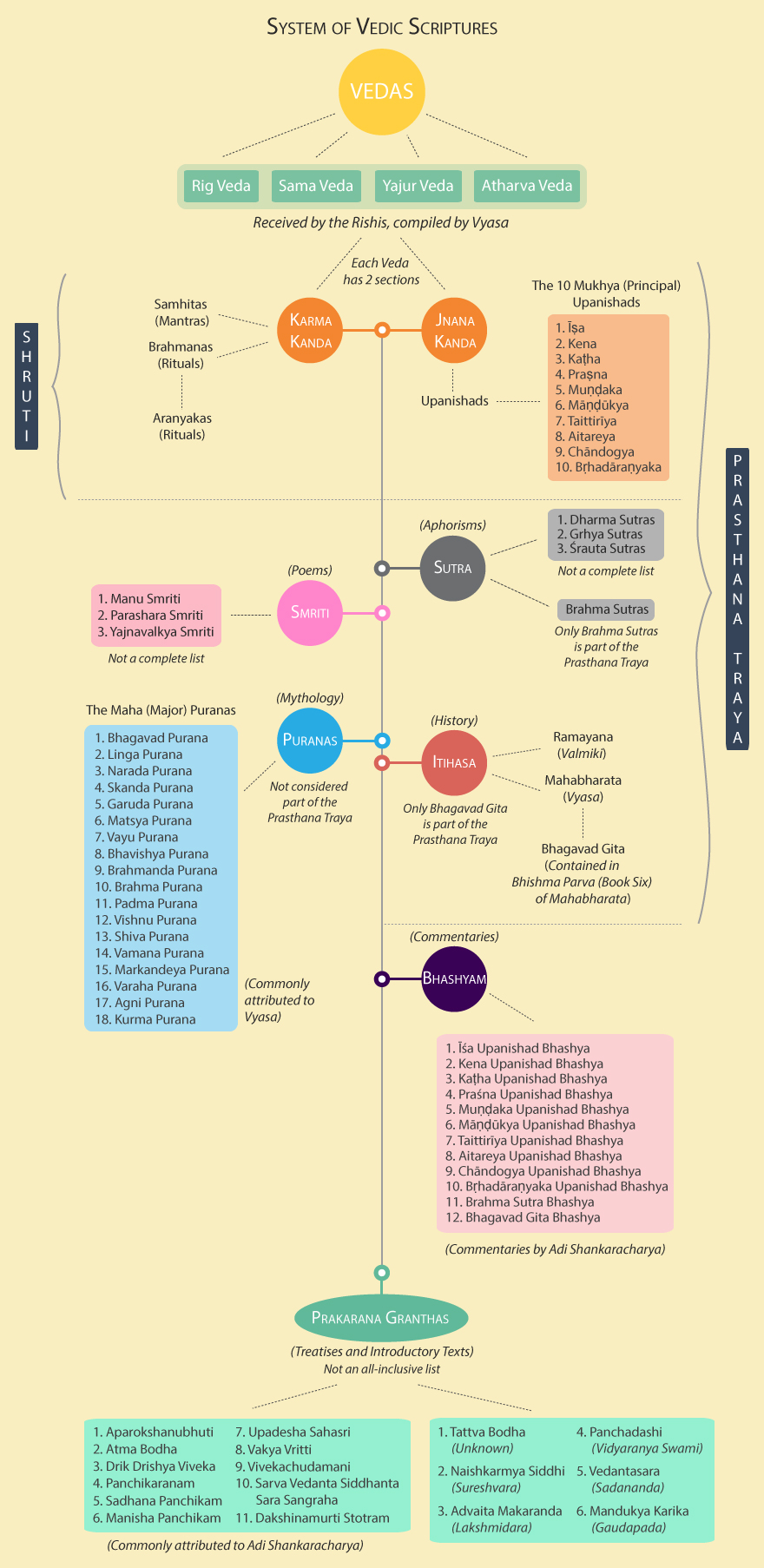
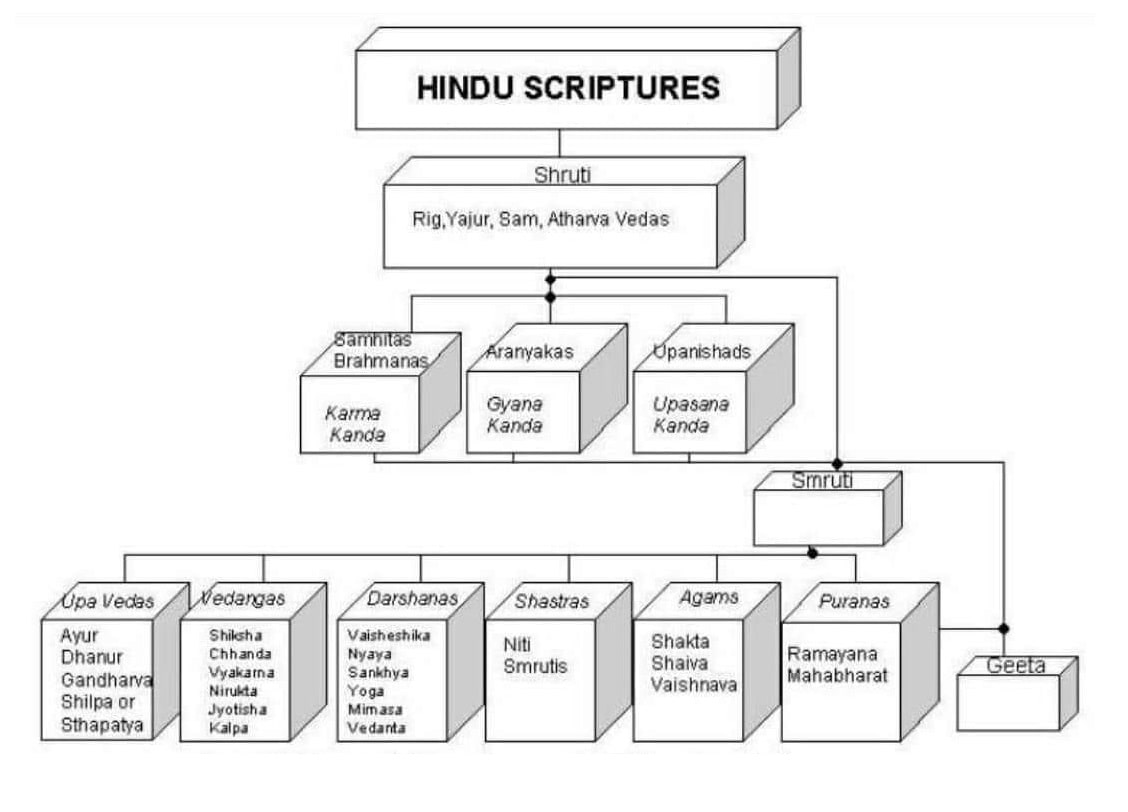
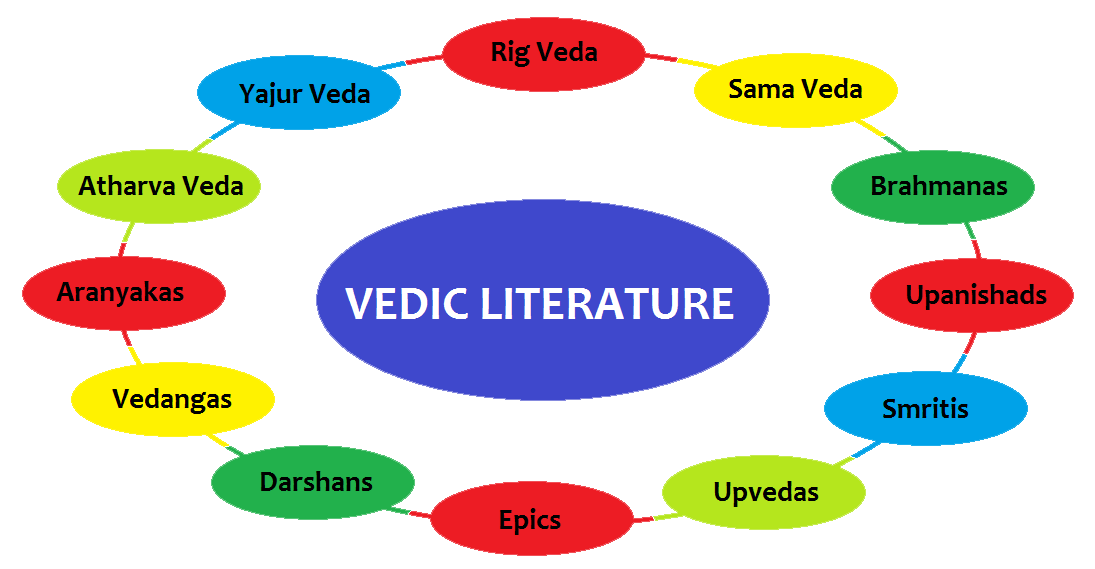
The Vedic literature consists of four Vedas, namely: Rig Veda, Sama Veda, Yajur Veda, and Atharva Veda. The mantra text of each of the Vedas is called Samhita. Types of Vedic Literature There are broadly two types of Vedic literature:

The Tree of Vedic Literature The Complete Lectures of Atmatattva Das Discourses on Vedic Wisdom
The term "Vedic" is derived from the Sanskrit word "Veda," which means knowledge or wisdom. The Vedic Literature is classified into four main categories: Samhitas, Brahmanas, Aranyakas, and Upanishads. Each category serves a specific purpose and contributes to the comprehensive understanding of Vedic philosophy and spirituality.
Early & Later Vedic Period & Vedic Literature (1500 to 600 B.C)
Nov 6, 2023 The Vedas are India's oldest known works of literature. The Vedas were written in Sanskrit and passed down orally from generation to generation. Vedic literature consists of four Vedas: the Rig Veda, the Yajur Veda, the Sama Veda, and the Atharva Veda. Each Veda is made up of the Brahmanas, Upanishads, and Aranyakas.

Pin by Sreedevi B on RISHI, MUNIS OF INDIA Hinduism, Hindu philosophy, Vedas india
The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical [1] [note 1] and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred. [2]

Forty Aspects of Veda and Vedic Literature in the Light of Maharishi’s Total Knowledge
The term 'Vedic literature' simply means literature based on or derived from the Vedas. The texts which constitute the Vedic literature are: 1. The four Vedas i.e. Samhitas, 2. the Brahmanas attached to each of the Samhitas, 3. the Aranyakas, and 4. the Upanishads. The Vedas The Rg-Veda, Samveda and Yajurveda are collectively known as Vedatrayi.

The Tree of Vedic Literature
Overview Test Series The Vedic Literature is classified into four Vedas: the Rig Veda, the Sama Veda, the Yajur Veda, and the Atharva Veda and their Samhita and the allied Literature based on or derived from the Vedas. However, Shruti and Smriti are two types of Vedic Literature.
Vedic Period (Vedic Age) The Aryans, Vedic Literature Indian History
That experience is expressed in the ancient Vedic literature.. These Unified Field Charts constitute a major unification of knowledge, showing at a glance how all the diversity of knowledge emerges from a unified source. Since the unified field is understood as a field of consciousness, and consciousness is the most fundamental level of each.

PPT Vedic Literature PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5538364
Vedic literature 867 works Search for books with subject Vedic literature. Search. Not in Library.. This is a chart to show the publishing history of editions of works about this subject. Along the X axis is time, and on the y axis is the count of editions published.
.jpg)
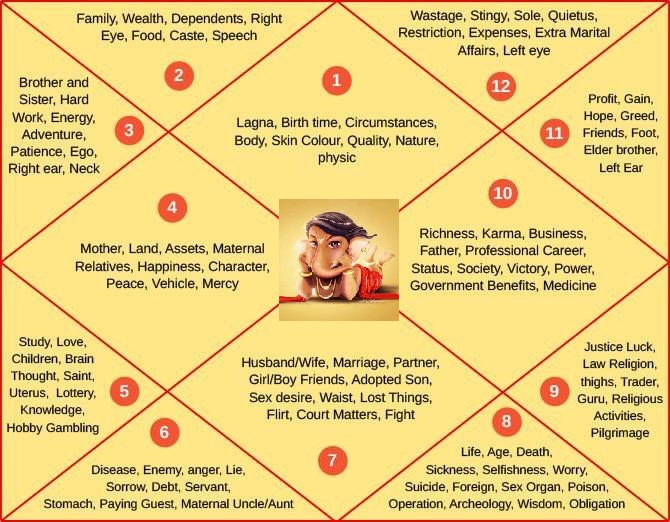
How to Read a Vedic Chart — Sydney Astrological Research Society
Vedas are earliest known literature. In Sanskrit, part of the linguistic group called Indo-European to which also along French, German, Latin, Persian and several others. The Vedas are traditionally regarded as Shruti. They are oral literature par excellence. Rig Vedic Literature

Vedas And Its Corollaries A Concise Illustration Of Sanatana Dharma Sahitya Indic Today
Vedic Sanskrit, also simply referred as the Vedic language, is an ancient language of the Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European language family. It is attested in the Vedas and related literature [1] compiled over the period of the mid- 2nd to mid-1st millennium BCE. [2]